15 KiB
Script setup-alpine
This script is the main install program for Alpine linux, only can run as root.
Table of Contents
- Script setup-alpine
- Setup scripts
- Licensing clarifications
- See also
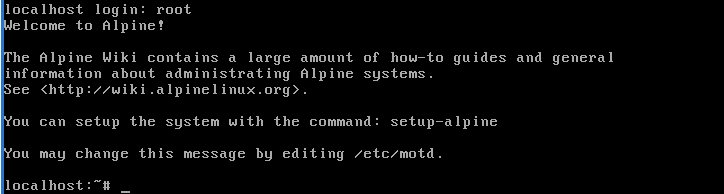
Log in as root and press enter. No password will be asked for if you're running from the boot image.
Environment variables before run
At the bash prompt you can export those environment variables that the scripts will handle it automatically:
Note The followin variables are only handle by
setup-diskandsetup-bootable
BOOTFSThe filesystem to use on/boot, defaults toext4, also allowsext2,ext3, (flat)btrfs,xfs.BOOTLOADERThe bootloader to use. Defaults tosyslinuxuntil 3.12 and since 3.14 defaults togrub, unless UEFI is used wil be forced to.BOOTSIZEThe size of/bootpartition when the scripts try to automatically created, its handle in Megs only.DISKLABELThe type of partition table to use. Defaults todos, unlesgruband UEFI is used, in which casegptis setup.ROOTFSThe filesystem to use on/, defaults toext4, also allowsext2,ext3, (flat)btrfsandxfs.USE_EFIEnable this to force using UEFI](alpine-boot-uefi-bios.md), so then automatically the bootloader will begruband partition wil begptthen.
Note The following variables one only supported by the
setup-alpineand others
KEYMAPOPTSsetup the keymap layout pair forsetup-keymap, by example="us us"HOSTNAMEOPTSsetup and parse forsetup-hostnamescript, by example="-n venenux"TIMEZONEOPTSsetup the timezone forsetup-timezonescript like="-z UTC"PROXYOPTSsetup and parse option tosetup-proxyscript like="http://webproxy:8080"DISKOPTSsetup and parse option tosetup-diskscript like="-m data /dev/sda"
Warning Check the complete support of scripts from Setup scripts section.
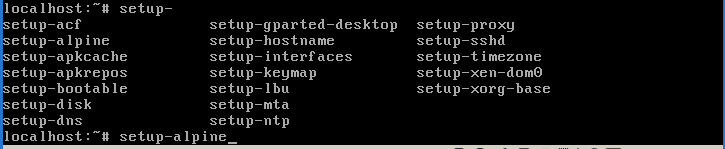
Running setup alpine script
Run the setup-alpine script as shown in the image:
The script interactively walks the user through executing several auxiliary setup-* scripts, in the order shown below.
The bracketed options represent example configuration choices, formatted as they
may be supplied when manually calling the independing setup scripts,
or using a setup-alpine "answerfile" using the variable environments prevously cited.
-hShows the up-to-date usage help message.-c <answerfile>Create new answerfile with default choices, you then edit and tune up.-f <answerfile>Use the new created answerfile, which may override some or all of the prompts.-qRun in "quick mode", will setup less question adn assumes defaults for rest.
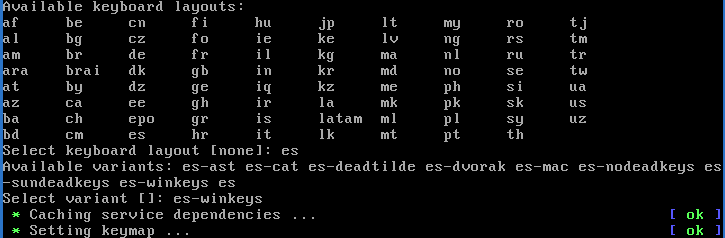
Select keyboard layout
Choose your keyboard layout. If you don't know your keyboard layout, choose us. Typically, for a Latin American environment, es is enough. For Russian (and maybe Cyrilic) ru is sufficient.
Note check
setup-keymapscript at Setup scripts section.
Select keyboard variant
Choose your keyboard variant. If you don't know your keyboard variant, choose the default from the list. For example, the typical Latin American keymap is es-winkeys.
Note check
setup-keymapscript at Setup scripts section.
Enter system hostname
Host name, which will be the name of your computer. using localhost is enough and recommended for testing purposes because permits apply mostly to how-tos and tutorials on the wiki pages.
Note check
setup-hotnamescript at Setup scripts section.
Initialize network cards
Choose your network card. Typically, you can just go with the default (press enter), a second question will ask about any other configuration. Type "no" then press enter to bypass the step to property set up after installation finished property.
IMPORTANT NOTE: mostly in x86 and x64 ISO images we can let
configurations for later, cos at the most modern the network card, the
lest supported or still not well tested. Just type done and press
enter. If you configured the wired interface, another question will be
asked, use dhcp? Most people will use DHCP, so press enter again. If
you have Internet connection from ISP, most settings are just DHCP, so
all will be configured automatically.
Note check
setup-networkingscript at Setup scripts section.
Warning check ../tutorials/alpine-tutorial-wifi-routering.md
Initialize network DNS
The DNS will be automatically detected, if not, you will be asked ask
for the server addresses. Type "" (empty string) for domain, then press
enter. Later you can change it to 8.8.8.8 (or the DNS server address
of your choice) as shown in the picture. Press enter to go to the next
question:
Note check
setup-dnsscript at Setup scripts section.
Changing the root password
Next a root password must be defined. You'll need to type it twice for
confirmation as the picture shows. If it's too short you will get a
warning, but your password will still work. Just retype it and go.
Note: when you type, NO chars will be shown.
Which timezone to choose?
Select a timezone, just press enter to use UTC when perform a single
installation.
Note check
setup-timezonescript at Setup scripts section.
Proxy chooser
Then setup script will ask for proxy chooser.. just type none and then
press enter
Note check
setup-proxyscript at Setup scripts section.
Enter mirror number
Then setup script will ask for repository mirror chooser.. just type
done and then press enter, this will be configure many times later
during usage of the system. Almost any tutorial of newbie pages will
explain detailed so lest bypass using "done".
Note check
setup-apkreposscript at Setup scripts section.
Which ssh server?
Installing an SSH server enables you to manage your machine remotely. OpenSSH is what the big distros use. Dropbear is a tiny SSH replacement. Recommended to type openssh and then press enter, because you able to connect using command line from Unix-like systems also is the offline available in all alpine installer images.
Note check
setup-sshdscript at Setup scripts section.
Which NTP client to run?
This is for time sync. Press enter to use the image offline. It can be changed after installation.
Note check
setup-ntpscript at Setup scripts section.
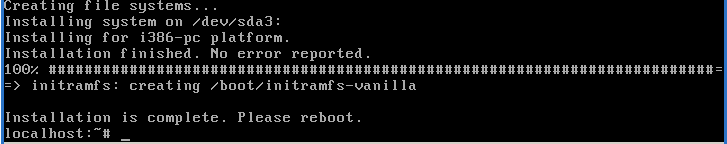
Script setup-disk choose the target device
This script its called at last from setup-alpine, it will mount a target device,
wil try to partitioned and copy the data to the target device.
Those are the questions that wil be prompt if you just invoke by default:
- disk to use "setup-disk" first question is to choose the disk destination ..
commonly
sda(/dev/sda) are the hard disk andsdbthe USB boot or CD/DVD image. - mode to use to choose the mode to install,
sysfor desktop/server,datafor live mixed mode, for more information check data modes section. - erase the disk This question will be promtp only if the disk already have
partitions, if you choose
ywill erase hole device and make new partitions. - formatin and coping later the script will copy all the data to the target
device, and the if you invoke from
setup-alpinewill callsetup-bootabletoo.
Check the setup disk next section for specific script options
After a while the installation will finish and alpine can be booted
Setup scripts
setup-hostname
setup-hostname [-h] [-n hostname]
setup-interfaces
setup-interfaces [-i < interfaces-file]
setup-dns
setup-dns [-h] [-d domain name] [-n name server]
setup-disk
This script its invoked by setup-alpine and as the same it support the
following enviroment variables:
DEFAULT_DISKThe device disk to use as target installation, default to=noneBOOTFSThe filesystem to use on/boot, defaults toext4, also allowsext2,ext3, (flat)btrfs,xfs.BOOTLOADERThe bootloader to use. Defaults tosyslinuxuntil 3.12 and since 3.14 defaults togrub, unless UEFI is used wil be forced to.BOOTSIZEThe size of/bootpartition when the scripts try to automatically created, its handle in Megs only.DISKLABELThe type of partition table to use. Defaults todos, unlesgruband UEFI is used, in which casegptis setup.ROOTFSThe filesystem to use on/, defaults toext4, also allowsext2,ext3, (flat)btrfsandxfs.USE_EFIEnable this to force using UEFI](alpine-boot-uefi-bios.md), so then automatically the bootloader will begruband partition wil begptthen.
Those are the most working options to parse to the script, only supported if you
runs directly, not if you parse it to setup-alpine script:
-m data | sysset the install mode target; check the data modes section-qExit quietly if no disks are found-vVerbose mode
Data modes
In "sys" mode, it's an installer, it permanently installs Alpine on the hole target partition,
in "data" mode, it provides a larger and persistent /var volume on the hole target partition.
data - Data Disk Mode
This mode runs OS from system RAM install media, but using swap and /var persistent.
If this mode is selected, script creates two partitions on the selected storage
device asked by setup-disk firts question, /var and swap respectivelly.
this setup is used for special server deploys or minimal devices deploys like ARM devices.
sys - System Disk Mode
This is a traditional hard-disk install.
If this mode is selected, script creates three partitions on the selected storage
device asked by setup-disk firts question, /boot, / and swap respectivelly.
this setup is used for generic desktop and development machines, or server bare metal deploys.
ram - Diskless Mode
This means the entire operating system with all applications are first loaded into RAM and then only run from there. This is the method already used to boot the .iso installation images, however setup-alpine can also configure the installed system to continue to boot like this if "disk=none" is specified.
Custom configurations and package installations may optionally still be preserved or "persist" across reboots by using the Alpine local backup tool lbu.
setup-timezone
setup-timezone [-z UTC | -z America/New_York | -p EST+5]
setup-proxy
setup-proxy [-hq] [PROXYURL]
setup-apkrepos
setup-apkrepos [-fhr] [REPO...]
setup-sshd
setup-sshd [-h] [-c dropbear|openssh|none]
setup-ntp
setup-ntp [-h] [busybox|openntpd|chrony|none]
setup-bootable
Setup boot loaders, it's not invoked directly by setup-alpine but
it triggers by setup-disk if you choose sys or data mode.
setup-bootable [-usfk] source [dest]
- The argument source can be a directory or an ISO (will be mounted to MNT or /mnt) or a URL (will be downloaded with WGET or wget).
- The argument dest can be a directory mountpoint, or will default
to
/media/usbif not supplied.
Those are the options:
-kKeep alpine_dev in syslinux.cfg; otherwise, replace with UUID.-uUpgrade mode: keep existing syslinux.cfg and don't run syslinux-fOverwrite syslinux.cfg even if -u was specified.-sForce the running of syslinux even if -u was specified.-vVerbose mode
Licensing clarifications
CC BY-NC-SA: the project allows reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format for noncommercial purposes only, and only so long as attribution is given to the creators involved. If you remix, adapt, or build upon the material, you must license the modified material under identical terms, includes the following elements:
- BY – Credit must be given to the creator of each content respectivelly, starting at the first contributor.
- NC – Only noncommercial uses of the work are permitted, with exceptions if you fill an issue here!
- SA – Adaptations must be shared under the same terms, you must obey this terms and do not change it.
https://codeberg.org/alpine/alpine-wiki/src/branch/main#license